Current Status of Myoelectric Prosthetic Hands
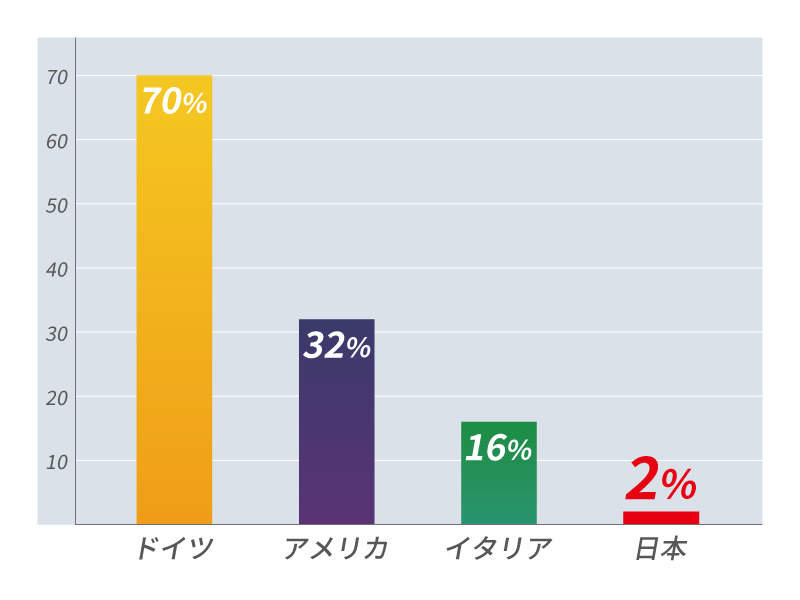
Source: Current status and issues of the spread of myoelectric prosthetic hands, strategies for high-level amputees, and future prospects
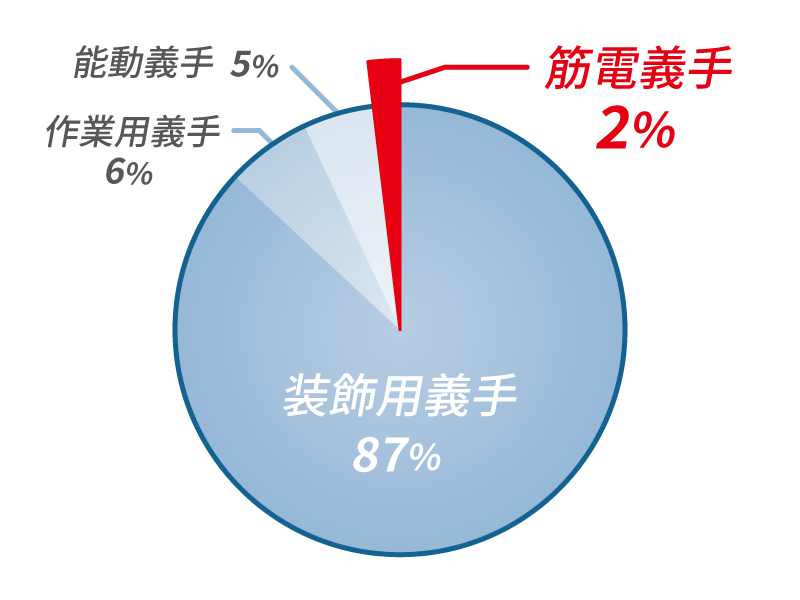
Source: Provision of myoelectric prosthetic hands and issues under the Act on Support for Independence of Persons with Disabilities
According to a survey by the Cabinet Office, there are 82,000 people with upper limb amputations over the age of 18 in Japan, and the number is increasing by approx. 3,000 every year. Regardless of the high demand, 70% of the 82,000 prosthetic hand users want a myoelectric prosthetic hand, its current penetration rate is only 2% due to various hurdles. (Source: Provision of myoelectric prosthetic hands and issues under the Act on Support for Independence of Persons with Disabilities)
Problems with Myoelectric Prosthetic Hands
Costs
Until now, if you want to buy a myoelectric prosthetic hand in Japan, your options are limited in prosthetic hands made overseas which cost from 1 million yen to a several million yen for each. In countries with a support system, a prosthetic hand with are available even if its main unit price is expensive, but in the case of Japan, users need to go through an examination to receive support since myoelectric prosthetic hands are classified as special prosthetic devices in Japan.
By the time you receive the support system, you will have to pay the initial cost at your own expense, use it in your daily life for about a year to prove that your life will be difficult without a myoelectric prosthetic hand. After all these processes, you finally can receive financial support. If you do not pass this examination, you will not be eligible for the support and you will have to bear the full amount of millions of yen, so the burden will be very big for users, especially for fast-growing children.
Appearance
Many of the conventional myoelectric prosthetic hands are designed with focusing on their performance such as hold an object with sufficient force or perform specific tasks, which make their appearance far from human arms. This is one of the reasons that Japanese people avoid myoelectric prosthetic hands since they care about the appearance strongly.
As you can see from the graph showing the ratio of the types of prosthetic hands selected by users, 86% of users selected cosmetic prosthesis which supplement the appearance but cannot perform practical movements. However, work prostheses and active prostheses that can perform practical movements at reasonable prices although they look very different from human arms, accounts only for about 10%.
Myoelectric prosthetic hands, which are characterized by a high variety of movements and strong gripping ability, make daily life very convenient for those with amputated arms. Also, a research reported that it helps for infants with congenital defects to develop their brain and muscle strength. (Source: Myoelectric prosthetic hand that expands the body: Aiming to realize technology that redefines “disability”)
It is necessary to spread myoelectric prosthetic hands free from these problems as soon as possible, and ALTs is tackling this urgent mission.
More details on the prosthetic hands proposed by ALTs
